But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
A government imposed price floor of 2 will result in.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Quantity demanded price per unit quantity supplied 10 5 50 20 4 40 30 3 30 40 2 20 50 1 10 a the price floor will not have an effect.
A price floor if set above the market equilibrium price means consumers will be forced to pay more for that good or service than they would if prices were set on free market principles.
If government imposes a price floor of 2.
A price floor example.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
D a surplus will result equal to 20 units.
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd.
Suppose the government sets the price of wheat at p f.
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor.
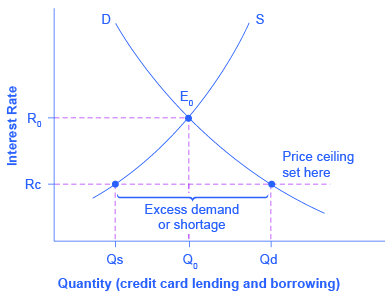
The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
B the price will fall to 1 because producers will be forced to incur losses.
A 0 10 tax levied on the sellers of chocolate bars will cause the.
When government laws regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices it is known as price control.
A price floor that is set above the equilibrium price creates a surplus.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
A government imposed price floor of 12 in this market results in supply curve for chocolate bars to shift up by 0 10.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
Figure 4 8 price floors in wheat markets shows the market for wheat.
Notice that p f is above the equilibrium price of p e.